
Features
Production
Research
Evaluating pepper cultivars for bacterial spot resistance
for bacterial spot resistance
March 13, 2008 By Marg Land
Bacterial spot is considered one
of the most destructive diseases of peppers and one of its strains can
also wreak havoc in field tomato plantings.
 |
| John Zandstra |
Bacterial spot is considered one of the most destructive diseases of peppers and one of its strains can also wreak havoc in field tomato plantings.
The disease, caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria, produces spots on plant leaves and fruit, defoliation of the plant, and can detrimentally affect plant growth, fruit yield and quality.
In light of this, researchers with the University of Guelph have been assessing, for many years, bacterial spot resistant pepper cultivars for suitability in commercial scale production.
In 2006, John Zandstra, a campus professor and researcher at Ridgetown College, located in Ridgetown, Ontario, evaluated four bell pepper cultivars resistant to bacterial spot: Double Up, Excursion II, ACX 270, and Snapper. They were compared to industry standards Aristotle (green standard) and King Arthur (early maturing).
The peppers were started in the greenhouse on May 4, 2006, and transplanted in the field June 12 using a single-row planting on plastic mulch. Nitrogen fertilizer was applied pre-plant at a rate of 60 kg/ha of actual N. Phosphorous and potassium was applied based on soil sampling. Four insecticide sprays were applied over the growing season to control European corn borer. The planting was supplemented with trickle irrigation with a target water application rate of one-inch per week.
The crop was harvested until October 10.
He reports that fruit number and yields were less than normal, most likely due to the late planting date. Plant vigour was average to below average and fruit size was also smaller.
No bacterial spot was present in the planting.
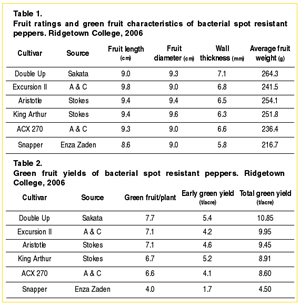
His results show Double Up, from Sakata Seed, was the top yielding cultivar with 10.9 T/acre. This cultivar is an early to mid-season variety with an average fruit size of 264 grams and a very thick fruit wall. Double Up also produced the most fruit per plant, 7.7, and had the greatest early yields, along with Aristotle.
The variety Excursion II, from Abbott and Cobb, had a yield of 9.5 T/acre with an average fruit size of 214 grams and a wall thickness of 6.8 mm. It is a more elongated variety, not as blocky.
The cultivar ACX 270, from Abbott and Cobb, produced 8.6 T/acre with an average fruit size of 236 grams and a wall thickness of 6.6 mm. This cultivar is also more elongated and less blocky.
Stokes Seeds’ Aristotle produced 9.5 T/acre with an average fruit size of 254 grams. This is a blocky variety and the industry standard for bell pepper production.
Zandstra says he hopes to repeat this experiment in 2007 using a double-row system.
| Bacterial spot
Bacterial spot is considered one of the most destructive diseases of peppers and one of its strains can also wreak havoc in field tomato plantings. The disease, caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris pv. Symptoms On stems and petioles, the lesions are black and elongated and can kill leaflets. Cause It infects the leaves of the pepper plant by entering through the The bacterium can spread in fields through water splashing, on the air Management |
Print this page